Risk-based Inspection (RBI)
Risk-based Inspection API 580 / API 581
The introduction of risk-based inspection in the petroleum industry gives advantages to security and economic feasibility.
The following works can be carried out :
- Training seminars for conducting a comprehensive technical examination of technological equipment based on a risk-based approach in refineries (standards API 580/581).The risk-based inspection (RBI) process and API 571 Damage Mechanisms and Damage
- Investigation.
- Demonstration of modern means of non-destructive testing used in the technical equipment diagnostics (TOFD (Time-of-Flight Diffraction), PA (phased array), PEC (pulsed eddy-current test), etc.).

Risk-based Inspection of hazardous industrial facilities.
Thus, facilities with a high probability of failure and serious consequences have a higher priority in inspection than facilities for which failure will not have serious consequences.
This technique allows the most efficient allocation of funds allocated for inspection and ensure the transition from Plan Preventive Maintenance (PPM) to preventive maintenance of equipment. The sources of standards applied by the companies in the Russian Federation are still industry reference books and state standards (GOST) developed by specialized institutes for various types of the equipment and certain branches. Most of them are outdated and do not meet modern requirements and technological processes. Thus, preventive maintenance methods come out on top for the of execution’s efficiency that allows western companies to minimize unforeseen accident by scheduling of preventive maintenance.
The basic documents for the implementation of inspection control by the method of the RBI are the standards of the American Petroleum Institute (API) – API 580/API 581. According to this document, risk-based inspection has the following objectives:
- Inspection of existing plant equipment in order to determine areas of high risk.
- Assessment of the risk associated with the operation of each unit of equipment at a refinery or petrochemical plant based on a consistent methodology.
- Prioritization of inspected equipment based on measured risk.
- Calculation of a suitable inspection program.
- Systematic risk management of equipment failure.
The probability analysis is based on a typical failure rate database for equipment types and includes a series of technical modules that assess the impact of specific failure mechanisms on failure probability and have the following functions:
- test work to determine the active failure mechanisms,
- determination of the environmental damage intensity,
- quantifying the effectiveness of the inspection program,
- calculation of the correction factor for applying to the frequency of typical failures.
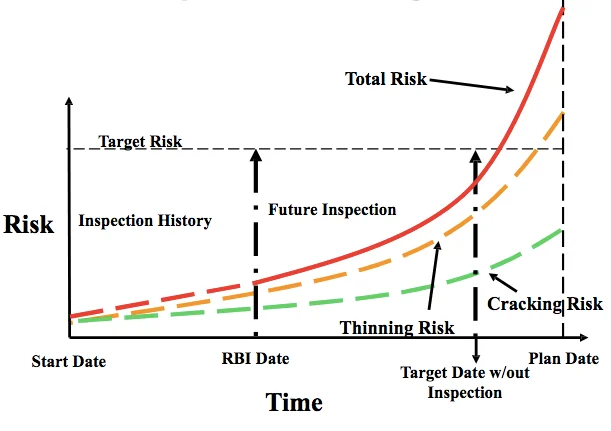
In the course of works on RBI inspection introduction specialists of our team:
- will form the criteria for equipment criticality based on the analysis of production processes and will select the most priority equipment for the current inspection;
- will help you to choose the best strategy for individual nodes and aggregates;
- will form necessary methods of service for the separate equipment (including repair costs, downtime and losses at various approaches: on fail or condition) for choice of the most effective method from the economy point of view;
- will develop a detailed description of the procedures for the diagnosis of actual technical condition of equipment;
- will develop regulations for inspections, including control points of measurement, deviation parameters, interpretation of the results, the procedure for action in case of fault detection;
- will make economic and environmental assessment of the condition-based maintenance application;
- will give recommendations on optimization of repair service processes, as well as theтdistribution of roles and responsibilities for the successful implementation of the methodology.
The application of the methodology RBI allows the management of facility to:
- monitor the actual current technical condition of the equipment;
- control the quality of performed repair and adjustment works;
- plan terms and content of repair and adjustment works;
- schedule the procurement time and required number of spare parts;
- reduce the need for on-hand stock of reserve parts and materials;
- improve reliability, extend the service life and maintenance period;
- get rid of the need for unscheduled repairs and production stops.